AI Help Me Out
RAG, Embedding, Agent
After attending webconf 2024 with some of my former colleagues, we noticed that although a few AI-related keywords were mentioned in the talks, most people still had a vague understanding of what AI is actually capable of.
They asked me if I could write a post to explain some of the concepts, so I created this slide deck.
AI Help Me Out – ai-hurry-up
The slides cover concepts like RAG, Embedding, and Tool Usage. They also briefly introduce the current trends, practical applications, where to find different models, and—most importantly—learning resources and methods.
A video version will be uploaded to YouTube later (hopefully it won’t be too awkward 🫠).
This article highlights a few key points from the slides.
LLM – Large Language Models
Large Language Models (LLMs) are deep learning models—especially based on the Transformer architecture—trained to understand, generate, and process natural language text. These models are usually pre-trained on massive datasets to learn statistical patterns and semantic structures in language.
Examples include GPT, Gemini, LLaMA, etc.
Embedding – Vector Representations
Have you ever wondered how a model can understand various types of input like text, images, or video?
It’s because of embedding, which converts diverse data types into vectors—numerical representations in multi-dimensional space.
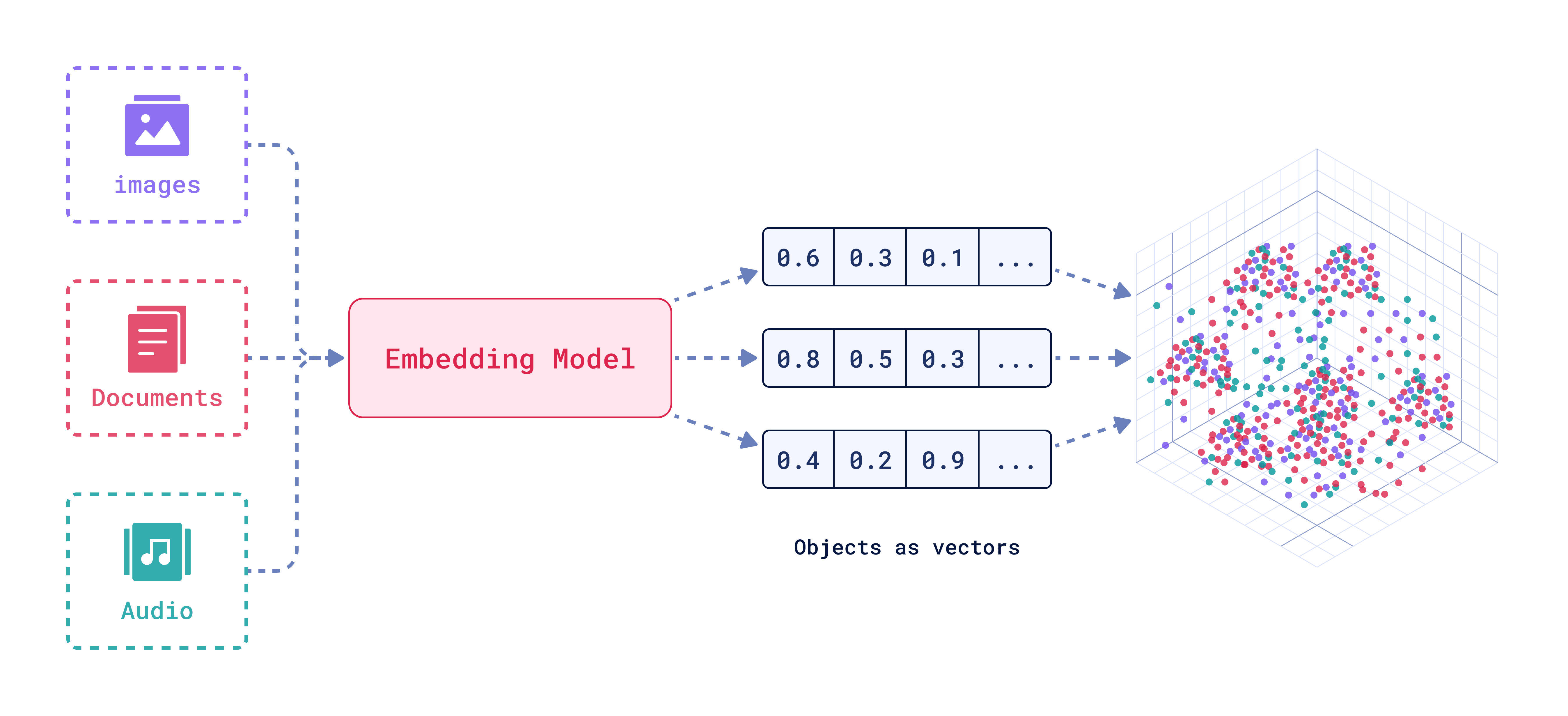
Still sounds a bit abstract?
Think of it this way: when you hear the word “dog,” you immediately imagine how a dog looks or sounds. That’s because your brain has built a kind of "embedding" that links the word to a concept.
Embeddings do the same—they connect text, sound, and visuals through mathematical relationships.
Check out ai-hurry-up for some fun examples you can try!
RAG – Retrieval-Augmented Generation
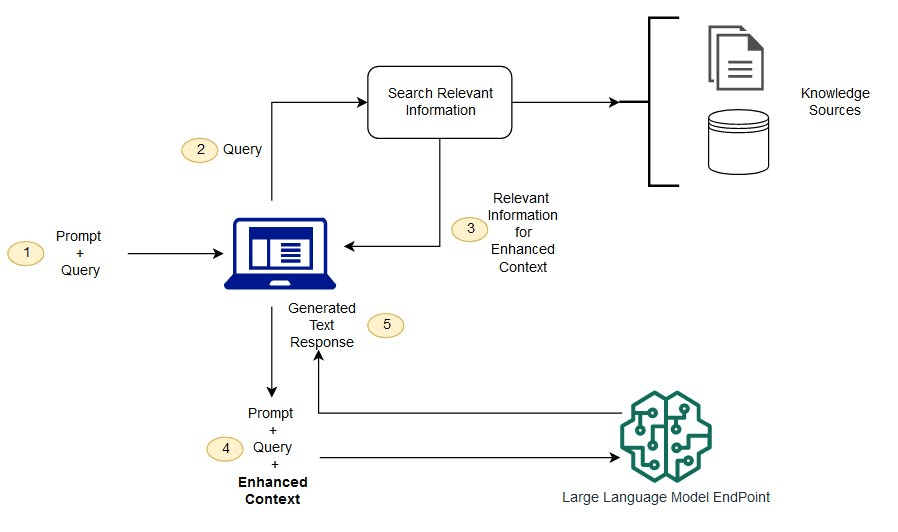
RAG is a complex topic—actually, it’s more of a framework. It uses embeddings to transform your data and store it in a vector database.
Yes, traditional databases can’t handle these transformed vectors, as they're just long sequences of numbers. Using SQL on them wouldn’t be meaningful, especially for finding semantic matches. That's why we use specialized vector databases.
RAG allows an LLM to search relevant vectorized information before generating a response.
What Problem Does RAG Solve?
LLMs often give off-topic answers or hallucinate facts—they’re not aware of real-time or domain-specific data.
RAG solves this by allowing the model to retrieve relevant data first, then answer based on it.
Challenges of RAG
- Input size limitations
- Parsing speed
- Complexity of vector databases
- Data filtering
Even with these challenges, RAG is being adopted rapidly.
Tools like Gmail Gemini and Notion AI already incorporate RAG. Some even propose newer frameworks like CAG.
Agent – AI Agents
This refers to AI systems that can make decisions and take actions independently. In short, it means giving an LLM the ability to use tools to complete tasks assigned by humans.
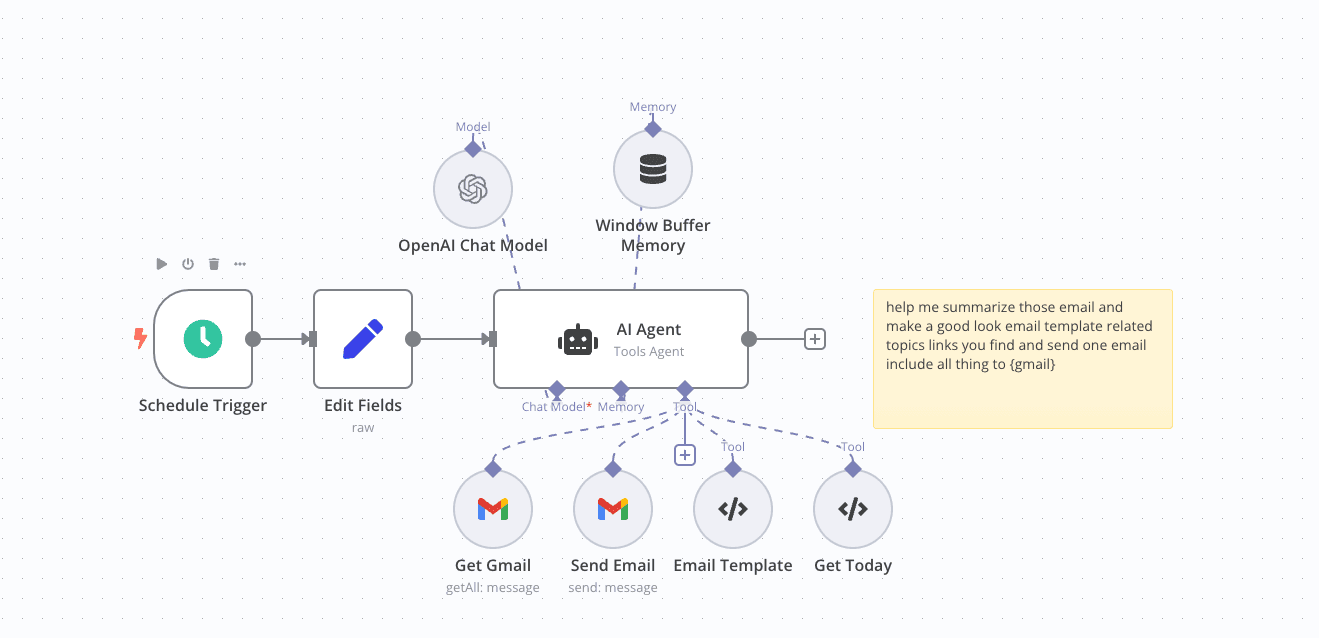
For example, in the image above I used n8n (a free, open-source workflow automation tool) to connect to GPT-4o. I had it parse the AI tech emails I subscribe to daily, extract the key points, and send them back to me.
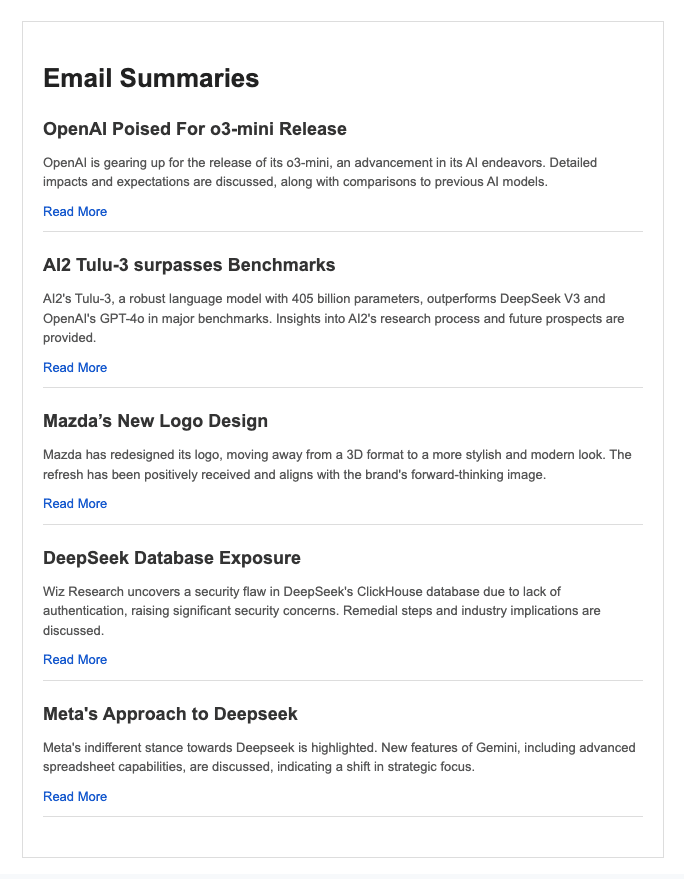
Of course, this is just a simple demo—real-world use cases can be much more complex.
Who knows? Maybe one day we’ll have Engineer Agents 😈
Summary
Using simple language, this post introduces several trending AI concepts to help you understand what these technologies can actually do:
- LLM – Large Language Models
Like a super brain that can chat with you. It understands and generates natural language so we can interact with computers in human language. Examples: GPT, Gemini, LLaMA.
- Embedding – Vector Representations
Imagine how hearing “dog” instantly brings up images and sounds in your mind. AI does this too, by turning various data (text, images, audio) into numeric vectors so computers can understand and connect them.
- RAG – Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Sometimes LLMs give wrong or random answers. RAG helps by retrieving the right info first and generating answers based on that, improving accuracy and relevance.
- Agent – AI Agent Systems
Think of it as a super helper that can decide what to do, how to do it, and which tools to use—like letting an AI auto-summarize your emails every day using tools like n8n.

