Tokenizer
A tokenizer is a tool that converts text into tokens, which can be words, subwords, or characters, serving as the basic input units for NLP models.
This article analyzes Tokenizer to understand how LLMs perceive input, as human understanding differs from model understanding. By exploring Tokenizer, we can gain deeper insights into how models view input data.
Token
In the previous article, we briefly mentioned the concept of tokens. A token is a basic unit, an abstraction of words that can be words, subwords, or characters. In NLP, the process of converting text into tokens is called tokenization.
What is a Tokenizer?
Imagine a vending machine. You press the button labeled "Soda," but the machine doesn't know what "Soda" means. Internally, it has translated your button press into a number, such as 001, which triggers the release of your drink. Similarly, a tokenizer converts our text into numerical values (IDs) so that computers can "understand" and process human language.
You can visit this website to experiment with different tokenizers and see varying results
Token Segmentation
Each character in the example represents a token, and combining these tokens forms a sentence. The difference is influenced by the tokenizer algorithm. There are many types of tokenizers, and different tokenizers produce different tokenization results.
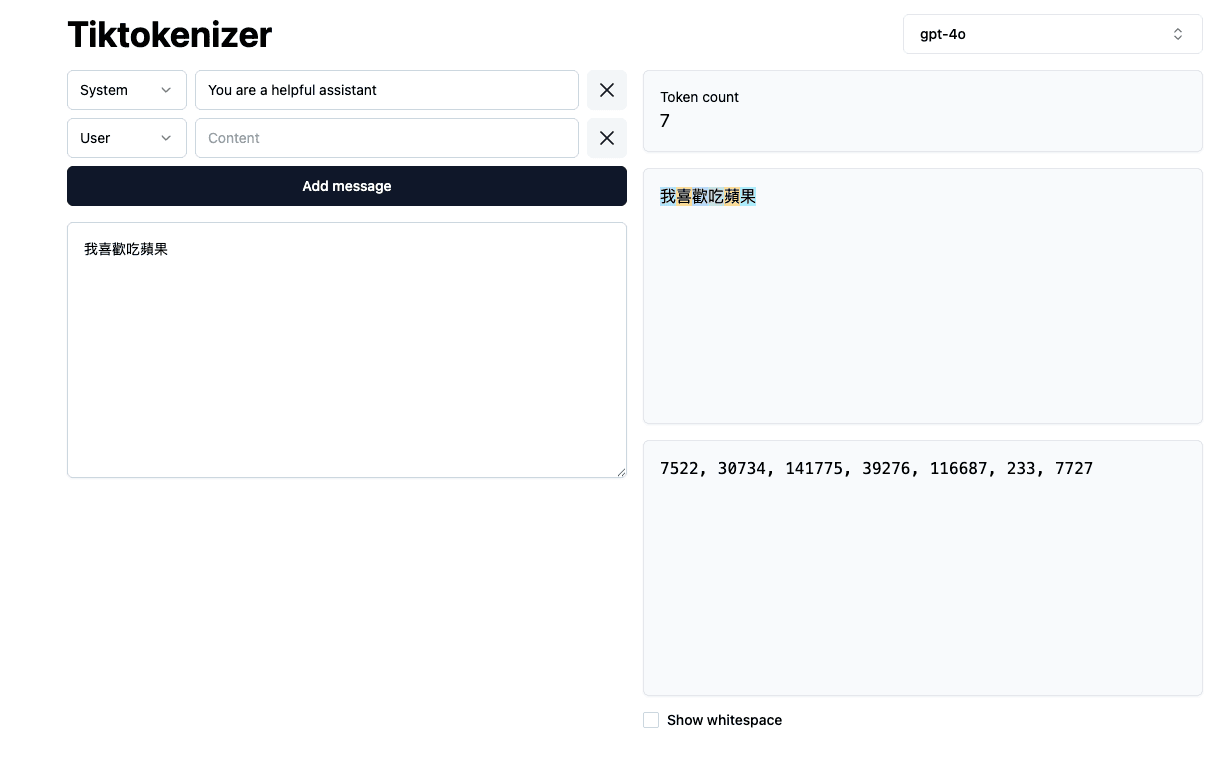
Token to Numerical ID Conversion
In the image above, we can see that the tokenizer converts text into tokens and then converts tokens into numbers. This is because models can only process numbers, not text.
After characters are converted to numbers, we can use these numbers as model inputs for training or prediction. This involves inference, where we predict the next number that will appear through numerical indices, then convert the numbers back to characters to generate text.
Tokenizers are specific to the language models they are built for, so the choice of tokenizer is crucial when training models. There is no such thing as a universal tokenizer! Moreover, the choice of tokenizer affects vocabulary size and computational efficiency.
Types of Tokenizers
- Word Tokenizer: Splits text into words. -> 我喜歡吃蘋果 -> '我', '喜歡', '吃', '蘋果'
- Character Tokenizer: Splits text into characters. -> 我喜歡吃蘋果 -> '我', '喜', '歡', '吃', '蘋', '果'
- Subword Tokenizer: Splits text into subwords. -> 我喜歡吃蘋果和芒果 -> '我', '喜', '歡', '吃', '蘋', '果', '和', '芒', '果'
Text is decomposed based on its granularity, and tokenizers for different languages also vary. For example, Chinese tokenizers may split a character into multiple subwords, while English tokenizers split a word into multiple subwords. In some cases, a Chinese token might be a single character, while in others it might be a word, depending on the tokenizer's design. This is one of the main challenges faced in Chinese model development.
Can Everything be Tokenized?
- Language Ambiguity: Due to the inherent ambiguity in human language, tokenizers may produce different tokenization results.
- Is it dangerous to pilot an aircraft, or are aircraft in flight dangerous?
- Languages without clear boundaries (such as Chinese and Japanese): In these languages, there are no clear separators between words, making tokenization difficult. How do we determine where one word ends and another begins?
What Can We Do After Tokenization?
- Search Engines: When you input a query into search engines like Google, they use tokenization to parse your input. This breakdown helps search engines filter through billions of documents to present you with the most relevant results.
- Speech Recognition: Voice assistants like Siri or Alexa heavily rely on tokenization. When you ask a question or give a command, your spoken words are first converted to text. This text is then tokenized, allowing the system to process and act upon your request.
- Machine Translation: Tools like Google Translate utilize tokenization to segment sentences in the source language. After tokenization, these segments can be translated and then reconstructed in the target language, ensuring the translation preserves the original context.
- Sentiment Analysis: Tokenization plays a crucial role in extracting insights from user-generated content, such as product reviews or social media posts. For example, a sentiment analysis system for an e-commerce platform might tokenize user reviews to determine whether customers are expressing positive, neutral, or negative sentiments.
Conclusion
Tokenization is the fundamental infrastructure for processing textual data in artificial intelligence. By breaking down text into tokens that computers can understand through tokenization, AI models can perform various NLP tasks such as translation, summarization, and conversation. As AI technology advances, tokenization methods have become increasingly sophisticated, evolving from early word tokenization to current subword tokenization to better handle rare words, abbreviations, and multilingual text.
The efficiency and accuracy of tokenization are also crucial for AI model performance, affecting training speed, inference speed, and result quality. If you're interested, feel free to check out the reference materials below!

